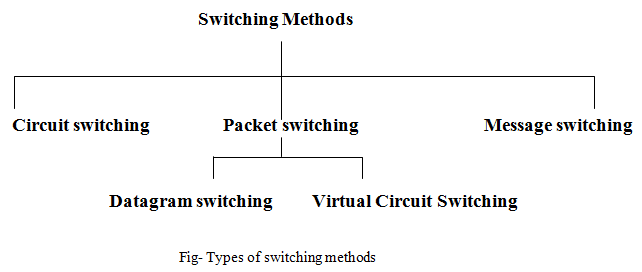
Switching techniques in data communication
Switching techniques
Switched communication networks are those in which data transformed from source to destination is routed between various intermediate nodes.
In large network , there can be multiple paths from sender to receiver. The switching techniques will decide the best route for data transmission.
There are mainly three typical Switching Techniques available for digital traffic:
- Circuit Switching
- Message Switching
- Packet Switching
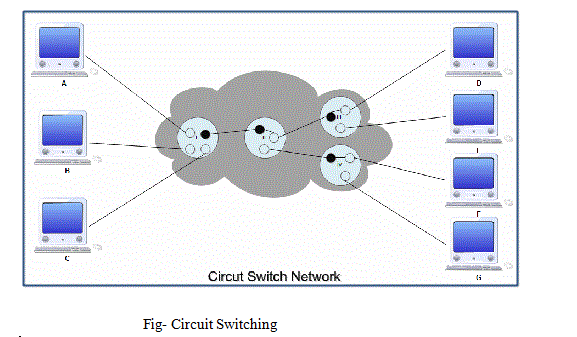
1) Circuit Switching
- Circuit Switching is a technique that directly connects the sender and the receiver in an unbroken path.
- For example take telephone switching equipment establishes a path that connects the caller’s and reciever’s telephone by making a physical connection.
- Routing decisions in circuit must be made when the circuit is first established, but there are no decisions made after that time.
- A complete end to end path must exist before communication can take place.
- Once the connection has been initiated and completed, the destination device must acknowledge that it is ready and able to carry on a transfer.
Advantages:
- The communication channel is end to end dedicated
Disadvantages:
- More bandwidth is required.
- Connection establishment time is more.
- More expensive than any other switching techniques because a dedicated path is required for each connection.
- Inefficient use of communication channel.
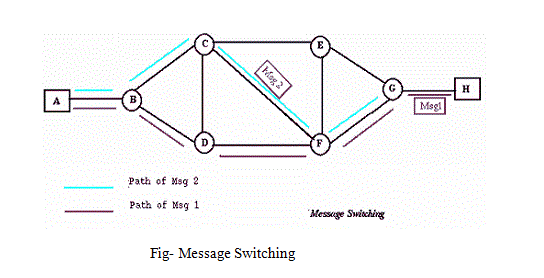
2) Message Switching
- In message switching there is no dedicated path required between two communicating devices, because the message switching is the follow the connectionless network.
- With message switching there is no need to establish dedicated path between two stations.
- When a station sends a message, the destination address is appended to the message.
- The message is then transmitted through the network in its entirety, from node to node.
- Each node receives the entire message, stores it in its entirety on disk and then transmits the message to the next node. This type of network is called a store and forward network.
Advantages:
- Efficient traffic management.
- Large storing capacity required.
Disadvantages:
- Is not compatible with interactive applications.
- Store and forward devices are example.
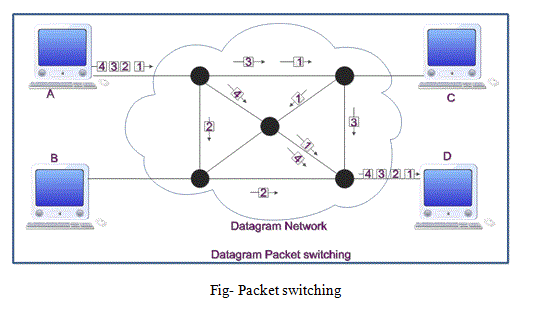
3) Packet Switching
- In packet switching message are broken up into packet.
- Each packet is tagged with appropriate source and destination address.
- Individual packets take different routes to reach the destination.
Packet switching: Datagram
- Datagram packet switching is a packet switching technology by which each packet is treated as a separate entity and are called as datagram.
- Packets have their own complete addressing information attached.
- Each packet follows different routes to reach the destination.
- So, the packets may arrive at different times, and may be in a disturbed order. In this case reordering is done.
Packet switching: Virtual
- In this type of switching a preplanned route is established before the packets are sent.
- Sender sends a "call request packet"to establish a logical connection and receiver sends back an acknowledgement packet "packet accepted".
- It is a cross between circuit switching network and packet switching network.
Advantages:
- Packet switching is cost effective.
- Offers improved delay characteristics.
- Packet can be rerouted if any problem occurs.
Disadvantages:
- Packet switching protocols are typically more complex.
- If packet gets lost sender needs to resend the data.

Comments
Post a Comment