Paging in OS
Paging
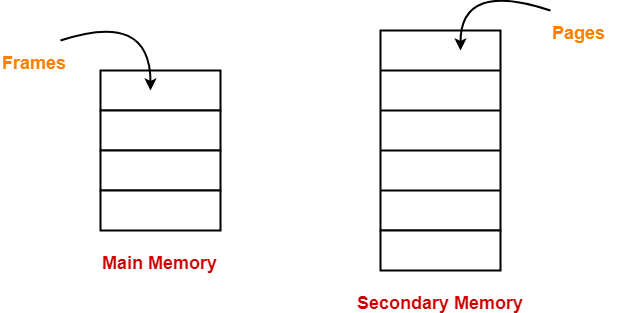
- Paging is a fixed size partitioning scheme.
- In paging, secondary memory and main memory are divided into equal fixed size partitions.
- The partitions of secondary memory are called as pages.
- The partitions of main memory are called as frames.
- Each process is divided into parts where size of each part is same as page size.
- The size of the last part may be less than the page size.
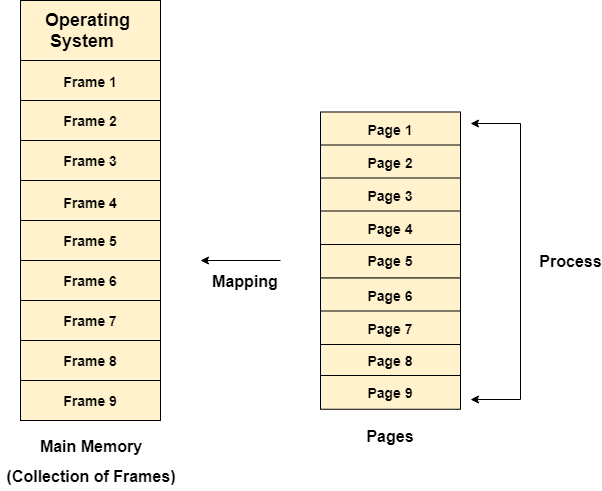
- The pages of process are stored in the frames of main memory depending upon their availability.
- Different operating system defines different frame sizes. The sizes of each frame must be equal. Considering the fact that the pages are mapped to the frames in Paging, page size needs to be as same as frame size.
Example-
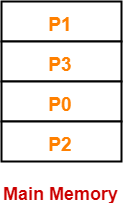
- Consider a process is divided into 4 pages P0, P1, P2 and P3.
- Depending upon the availability, these pages may be stored in the main memory frames in a non-contiguous fashion as shown-
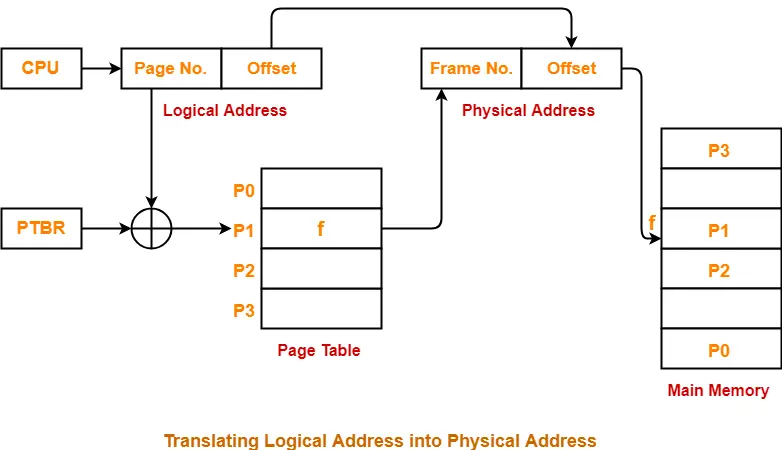
Translating Logical Address into Physical Address-
- CPU always generates a logical address.
- A physical address is needed to access the main memory.
Following steps are followed to translate logical address into physical address-
Step-01:
CPU generates a logical address consisting of two parts-
- Page Number
- Page Offset
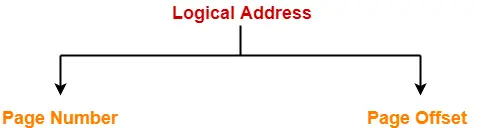
- Page Number specifies the specific page of the process from which CPU wants to read the data.
- Page Offset specifies the specific word on the page that CPU wants to read.
Step-02:
For the page number generated by the CPU,
- Page table provides the corresponding frame number (base address of the frame) where that page is stored in the main memory.
Step-03:
- The frame number combined with the page offset forms the required physical address.
- Frame number specifies the specific frame where the required page is stored.
- Page Offset specifies the specific word that has to be read from that page.
Diagram-
The following diagram illustrates the above steps of translating logical address into physical address-
Advantages-
The advantages of paging are-
- It allows to store parts of a single process in a non-contiguous fashion.
- It solves the problem of external fragmentation.
Disadvantages-
The disadvantages of paging are-
- It suffers from internal fragmentation.
- There is an overhead of maintaining a page table for each process.
- The time taken to fetch the instruction increases since now two memory accesses are required.
Thank you viewers..
This is published by soumy Sinha...

Comments
Post a Comment