Compaction in OS
Compaction
Compaction is a process in which the free space is collected in a large memory chunk to make some space available for processes.
- In memory management, swapping creates multiple fragments in the memory because of the processes moving in and out.
- Compaction refers to combining all the empty spaces together and processes.
- Compaction helps to solve the problem of fragmentation, but it requires too much of CPU time.
- It moves all the occupied areas of store to one end and leaves one large free space for incoming jobs, instead of numerous small ones.
- In compaction, the system also maintains relocation information and it must be performed on each new allocation of job to the memory or completion of job from memory.
Compaction is a process in which the free space is collected in a large memory chunk to make some space available for processes.
- In memory management, swapping creates multiple fragments in the memory because of the processes moving in and out.
- Compaction refers to combining all the empty spaces together and processes.
- Compaction helps to solve the problem of fragmentation, but it requires too much of CPU time.
- It moves all the occupied areas of store to one end and leaves one large free space for incoming jobs, instead of numerous small ones.
- In compaction, the system also maintains relocation information and it must be performed on each new allocation of job to the memory or completion of job from memory.
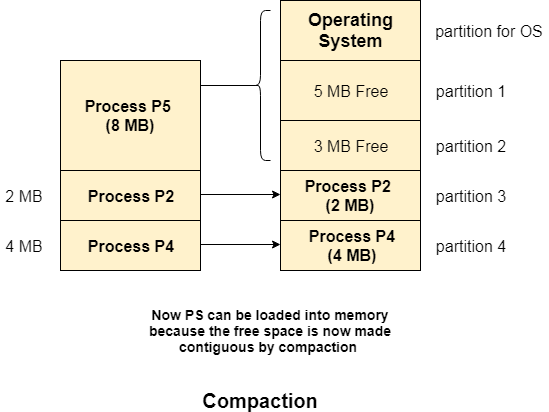
- compaction is used to minimize the probability of external fragmentation. In compaction, all the free partitions are made contiguous and all the loaded partitions are brought together.
-By applying this technique, we can store the bigger processes in the memory. The free partitions are merged which can now be allocated according to the needs of new processes. This technique is also called defragmentation.

As shown in the image above, the process P5, which could not be loaded into the memory due to the lack of contiguous space, can be loaded now in the memory since the free partitions are made contiguous.
Problem with Compaction
The efficiency of the system is decreased in the case of compaction due to the fact that all the free spaces will be transferred from several places to a single place.
Huge amount of time is invested for this procedure and the CPU will remain idle for all this time. Despite of the fact that the compaction avoids external fragmentation, it makes system inefficient.
Let us consider that OS needs 6 NS to copy 1 byte from one place to another.
- 1 B transfer needs 6 NS
- 256 MB transfer needs 256 X 2^20 X 6 X 10 ^ -9 secs
hence, it is proved to some extent that the larger size memory transfer needs some huge amount of time that is in seconds.

Comments
Post a Comment