Segmentation in OS
SegmentationIn operating system, Segmentation is a memory management technique in which, the memory is divided into the variable size parts. Each part is known as segment which can be allocated to a process.
The details about each segment are stored in a table called as segment table. Segment table is stored in one (or many) of the segments.
Segment table contains mainly two information about segment:
Why Segmentation is required?
Till now, we were using Paging as our main memory management technique. Paging is more close to Operating system rather than the User. It divides all the process into the form of pages regardless of the fact that a process can have some relative parts of functions which needs to be loaded in the same page.
Operating system doesn't care about the User's view of the process. It may divide the same function into different pages and those pages may or may not be loaded at the same time into the memory. It decreases the efficiency of the system.
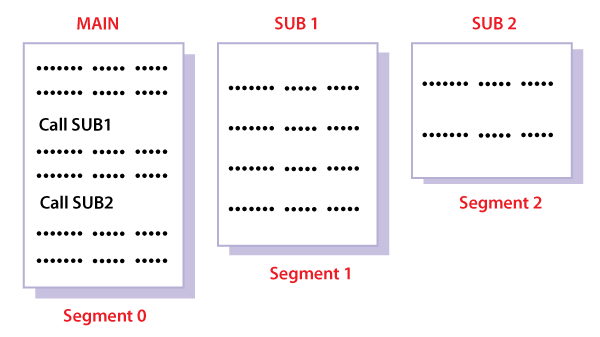
It is better to have segmentation which divides the process into the segments. Each segment contain same type of functions such as main function can be included in one segment and the library functions can be included in the other segment,
Translation of Logical address into physical address by segment table
CPU generates a logical address which contains two parts:
The Segment number is mapped to the segment table. The limit of the respective segment is compared with the offset. If the offset is less than the limit then the address is valid otherwise it throws an error as the address is invalid.
In the case of valid address, the base address of the segment is added to the offset to get the physical address of actual word in the main memory.
Thank you viewers..
This is published by soumy Sinha..
|

Comments
Post a Comment