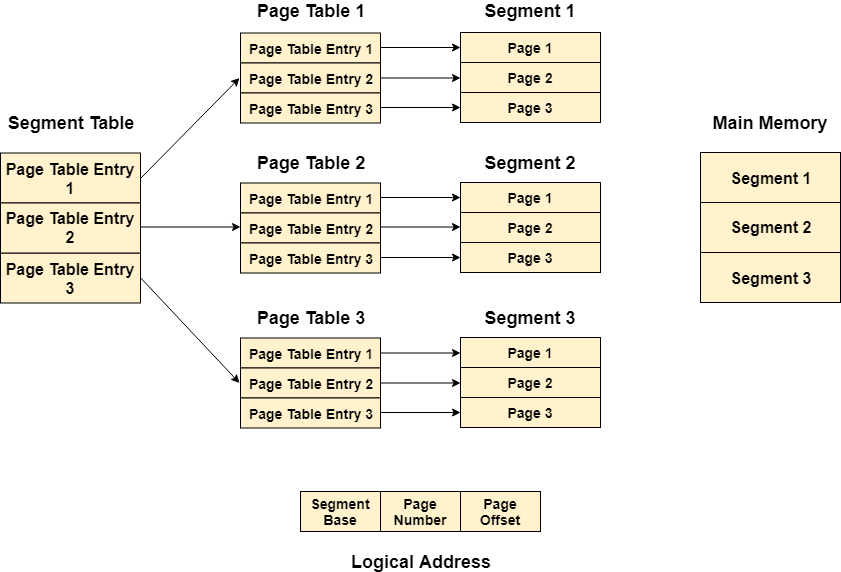
Segmented paged memory management In OS
Segmented Paging-
| Segmented paging is a scheme that implements the combination of segmentation and paging. |
Working-
In segmented paging,
- Process is first divided into segments and then each segment is divided into pages.
- These pages are then stored in the frames of main memory.
- A page table exists for each segment that keeps track of the frames storing the pages of that segment.
- Each page table occupies one frame in the main memory.
- Number of entries in the page table of a segment = Number of pages that segment is divided.
- A segment table exists that keeps track of the frames storing the page tables of segments.
- Number of entries in the segment table of a process = Number of segments that process is divided.
- The base address of the segment table is stored in the segment table base register.
- Pure segmentation is not very popular and not being used in many of the operating systems. However, Segmentation can be combined with Paging to get the best features out of both the techniques.
- In Segmented Paging, the main memory is divided into variable size segments which are further divided into fixed size pages.
- Pages are smaller than segments.
- Each Segment has a page table which means every program has multiple page tables.
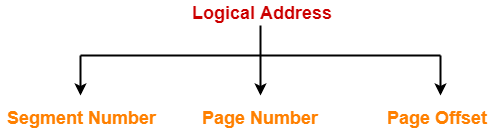
- The logical address is represented as Segment Number (base address), Page number and page offset.
Segment Number → It points to the appropriate Segment Number.
Page Number → It Points to the exact page within the segment
Page Offset → Used as an offset within the page frame
Each Page table contains the various information about every page of the segment. The Segment Table contains the information about every segment. Each segment table entry points to a page table entry and every page table entry is mapped to one of the page within a segment.
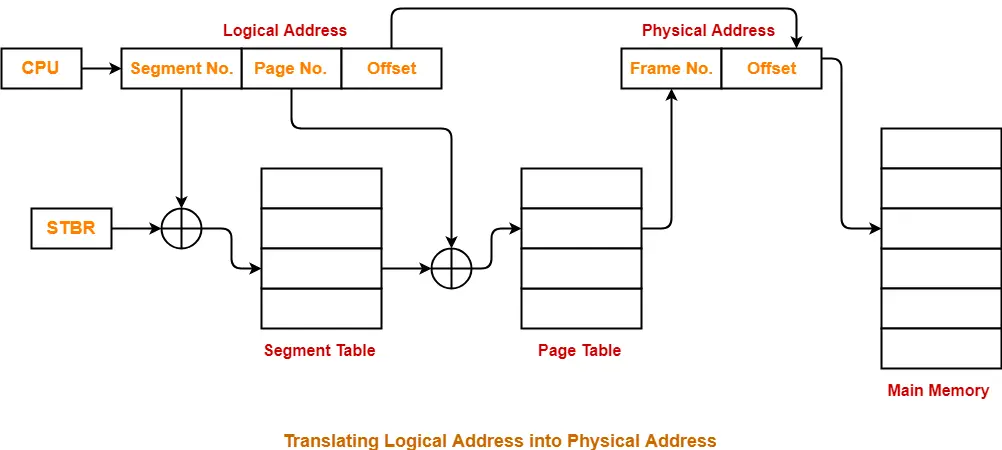
Translating Logical Address into Physical Address-
- CPU always generates a logical address.
- A physical address is needed to access the main memory.
Following steps are followed to translate logical address into physical address-
Step-01:
CPU generates a logical address consisting of three parts-
- Segment Number
- Page Number
- Page Offset
- Segment Number specifies the specific segment from which CPU wants to reads the data.
- Page Number specifies the specific page of that segment from which CPU wants to read the data.
- Page Offset specifies the specific word on that page that CPU wants to read.
Step-02:
- For the generated segment number, corresponding entry is located in the segment table.
- Segment table provides the frame number of the frame storing the page table of the referred segment.
- The frame containing the page table is located.
Step-03:
- For the generated page number, corresponding entry is located in the page table.
- Page table provides the frame number of the frame storing the required page of the referred segment.
- The frame containing the required page is located.
Step-04:
- The frame number combined with the page offset forms the required physical address.
- For the generated page offset, corresponding word is located in the page and read.
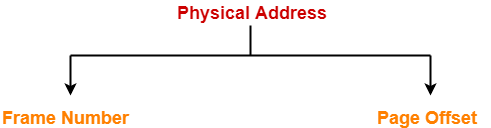
Diagram-
The following diagram illustrates the above steps of translating logical address into physical address-
Advantages-
The advantages of segmented paging are-
- Segment table contains only one entry corresponding to each segment.
- It reduces memory usage.
- The size of Page Table is limited by the segment size.
- It solves the problem of external fragmentation.
Disadvantages-
The disadvantages of segmented paging are-
- Segmented paging suffers from internal fragmentation.
- The complexity level is much higher as compared to paging.

Comments
Post a Comment