Types of properties of binary tree in data structure
Types of Properties of Binary Trees
- Rooted binary tree: It has a root node and every node has atmost two children.
- Full binary tree: It is a tree in which every node in the tree has either 0 or 2 children.
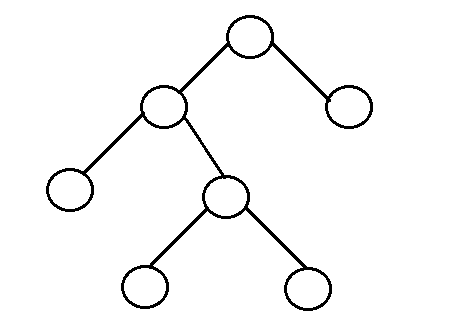
- The number of nodes, n, in a full binary tree is atleast n = 2h – 1, and atmost n = 2h+1 – 1, where h is the height of the tree.
- The number of leaf nodes l, in a full binary tree is number, L of internal nodes + 1, i.e, l = L+1.
- Perfect binary tree: It is a binary tree in which all interior nodes have two children and all leaves have the same depth or same level.
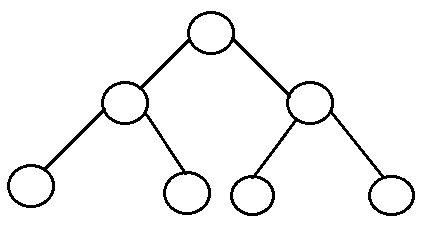
- A perfect binary tree with l leaves has n = 2l-1nodes.
- In perfect full binary tree, l = 2h and n = 2h+1 - 1 where, n is number of nod justes, h is height of tree and l is number of leaf nodes
- Complete binary tree: It is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
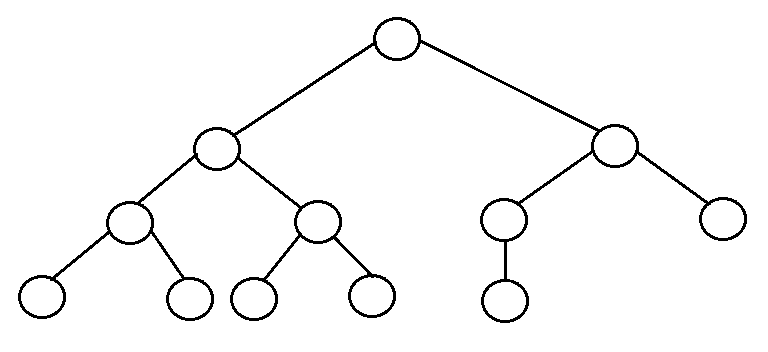
- The number of internal nodes in a complete binary tree of n nodes is floor(n/2).
- Balanced binary tree: A binary tree is height balanced if it satisfies the following constraints:
- The left and right subtrees' heights differ by at most one, AND
- The left subtree is balanced, AND
- The right subtree is balanced
An empty tree is height balanced.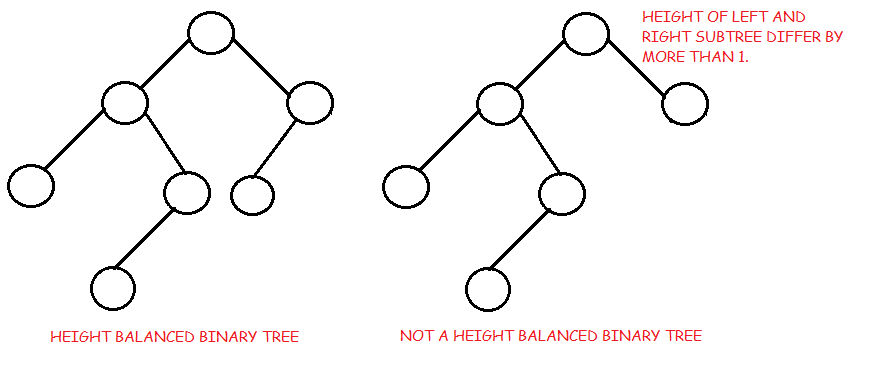
- The height of a balanced binary tree is O(Log n) where n is number of nodes.
- Degenarate tree: It is a tree is where each parent node has only one child node. It behaves like a linked list.
Thank you viewers..
This is published by soumy Sinha..
If you want to know more about data structure then pls subscribe our website and share with your friends..
For more information you can visit our FB page csviewers
And pls tell your next question we will definitely try to help you..

Comments
Post a Comment