Introduction of binary tree in data structure
Introduction To Binary Trees
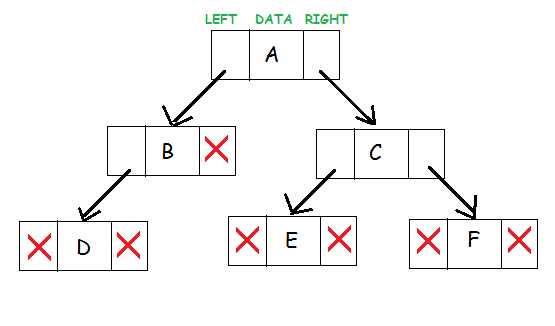
A binary tree is a hierarchical data structure in which each node has at most two children generally referred as left child and right child.
Each node contains three components:
- Pointer to left subtree
- Pointer to right subtree
- Data element
The topmost node in the tree is called the root. An empty tree is represented by NULL pointer.
A representation of binary tree is shown:
Common Terminologies
- Root: Topmost node in a tree.
- Parent: Every node (excluding a root) in a tree is connected by a directed edge from exactly one other node. This node is called a parent.
- Child: A node directly connected to another node when moving away from the root.
- Leaf/External node: Node with no children.
- Internal node: Node with atleast one children.
- Depth of a node: Number of edges from root to the node.
- Height of a node: Number of edges from the node to the deepest leaf. Height of the tree is the height of the root.
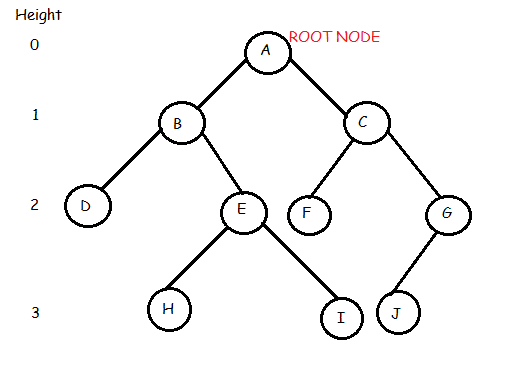
In the above binary tree we see that root node is A. The tree has 10 nodes with 5 internal nodes, i.e, A,B,C,E,G and 5 external nodes, i.e, D,F,H,I,J. The height of the tree is 3. B is the parent of D and Ewhile D and E are children of B.
Advantages of Trees
Trees are so useful and frequently used, because they have some very serious advantages:
- Trees reflect structural relationships in the data.
- Trees are used to represent hierarchies.
- Trees provide an efficient insertion and searching.
- Trees are very flexible data, allowing to move subtrees around with minumum effort.
Thank you viewers...
This is published by soumy Sinha..
Email id- soumysinha1002@gmail.com
If you want to more questions on data structure pls tell in comment box.
If this page is helpful for you then pls subscribe our page and share with your friends..
For know about more information and next question pls like our FB page ..
https://www.facebook.com/100038172142038/posts/115552203060517/?app=fbl

Comments
Post a Comment