INTRODUCTION TO LINKED LIST
Introduction to Linked Lists
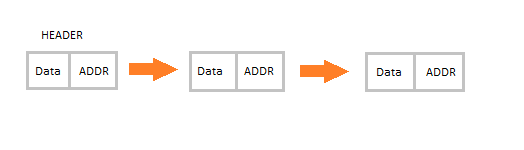
Linked List is a very commonly used linear data structure which consists of group of nodes in a sequence.
Each node holds its own data and the address of the next node hence forming a chain like structure.
Linked Lists are used to create trees and graphs.
Advantages of Linked Lists
- They are a dynamic in nature which allocates the memory when required.
- Insertion and deletion operations can be easily implemented.
- Stacks and queues can be easily executed.
- Linked List reduces the access time.
Disadvantages of Linked Lists
- The memory is wasted as pointers require extra memory for storage.
- No element can be accessed randomly; it has to access each node sequentially.
- Reverse Traversing is difficult in linked list.
Applications of Linked Lists
- Linked lists are used to implement stacks, queues, graphs, etc.
- Linked lists let you insert elements at the beginning and end of the list.
- In Linked Lists we don't need to know the size in advance.

Comments
Post a Comment